AI job search – Disrupting the Recruitment Status Quo: How jobstr.work and LLMs are Building the Future of Decentralised Job Searches
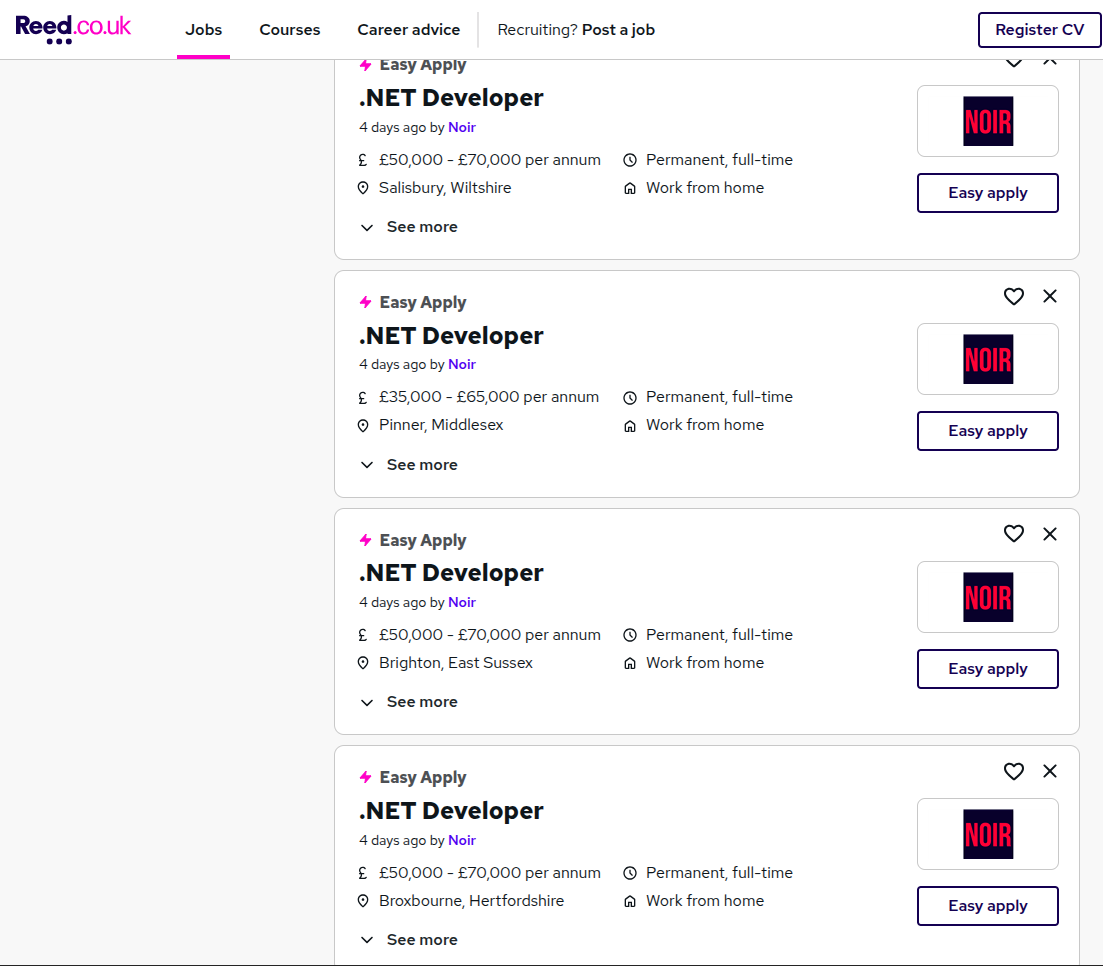
The traditional job search process “sucks” – it is characterised by closed platforms which creates a “recruitment shїtshow”. Don’t just take my words for that, try Indeed or Reed or LinkedIn!
Same job listed multiple times…
Remote, but different “location”
jobstr.work is a real solution, working via a decentralised platform for listing jobs that combines an open protocol with features designed to be friendly toward Large Language Models (LLMs).
This approach aims to create a robust, open standard for job discovery, moving away from reliance on single points of failure like the aforementioned “LinkedIn” or “Indeed”. Ps, in case you’re wondering, AI did NOT write this! 😃
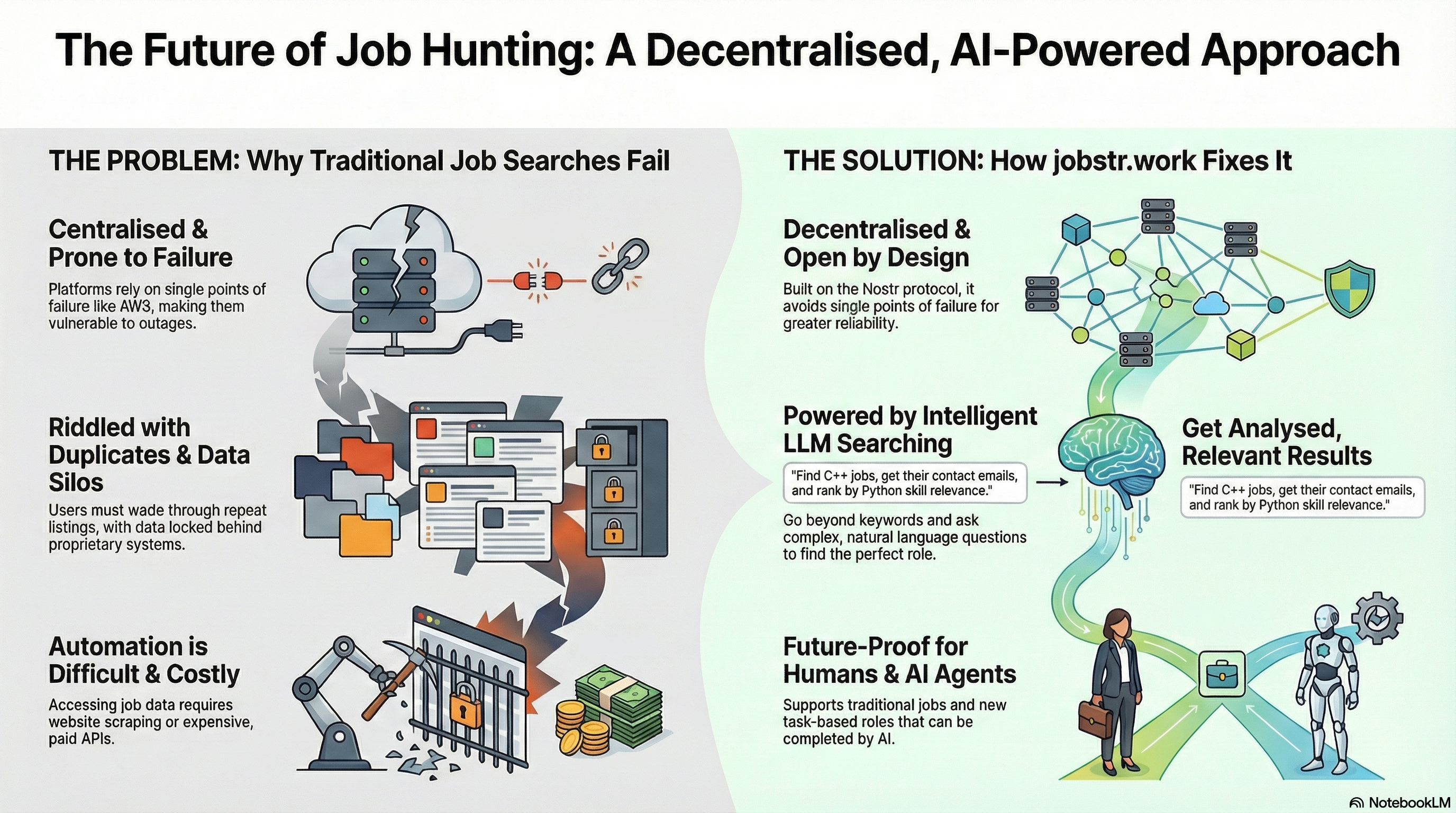
The Problem: Centralised Failures and Data Silos
Traditional job boards require users to wade through pages of adverts, errr…I mean listings, and the only way to automate any of this would be by scraping the sites or using proprietary paid APIs.
The jobstr.work model addresses this by providing access to a job listing site that operates without these constraints. Because the platform is decentralised, utilising multiple relays, it is designed not to fail during outages experienced by centralised providers like Cloudflare or Amazon AWS.

Bye bye LinkedIn !
The Decentralised Solution: Nostr and Structured Data
jobstr.work is built upon an open protocol, combining the idea that job listings need improvement with the architecture of the Nostr protocol. The platform uses structured data encoded in JSON LD. Job postings are published as Nostr events of kind 9993, which allows others using the Nostr SDK to standardise on the same event ID and display the listings.
Crucially, this architecture is schema.org compatible, basing its structure on Google’s existing schema.org/jobPosting standard. This compatibility ensures seamless integration with existing search and indexing systems.
Powering Job Search with LLMs and the MCP Server
The primary innovation of jobstr.work is its deep integration with LLMs, making it a powerful tool for modern job seekers.
- The MCP Server: The platform utilises an MCP server (Model Context Protocol server), which acts effectively as an API to the back end. The server (coded in Rust) must be running locally for so you can query the job listings using an LLM client.
- LLM Querying: Any LLM client, such as the command-line client Goose (which is what I demonstrated in the video), Claude, or ChatGPT, can be configured to interact with the MCP server via streamable HTTP. The LLM detects the available tools, referred to as extensions in Goose, such as
jobmcp. - Advanced Searching: Instead of simple keyword matching, users can ask complex, natural language questions. For instance, an LLM can be prompted to find jobs related to C++, fetch the corresponding contact email addresses, and then analyse the results to determine which listings are the best fit based on additional skills like Python. The LLM can interpret job details, stating that a particular role listing both C++ and Python is a “great fit,” while another position that does not list Python is “least relevant”.
We can also query internal metrics, such as retrieving the total number of listings (e.g., 13 jobs) or viewing top skills and companies.
The Hybrid Future: Task-Based Jobs for Humans and AI
jobstr.work is designed to be future-proof and extensible, specifically supporting task-based jobs that can be performed by either humans or AI agents. This feature allows recruiters to post jobs that an AI agent could perform, such as image analysis or text classification.
When posting a job, compensation can be specified per task. For human jobs, standard compensation details apply, but for AI agent jobs, the payment is strictly per task. Recruiters can post jobs by utilising the site (with a current payment of around $5 USD/£4 GBP via Stripe) or by using the Nostr SDK to post event kind 993. As the project grows, relays will be paid for from the proceeds of the listing fee – this is not just the right thing to do, it will also ensure greater robustness and quicker responses.
Conclusion
jobstr.work aims to remove the friction and reliance on scraping that plague the centralised job market listings online.
We can solve the “duplicates” problem by parsing the structured data output from Nostr with a prompt like “if you find duplicate descriptions, only show the oldest”.
Note: Ideally you build the client to list/retrieve listings up to 30 days old in the first instance.
Get fresh listings, and until a listing “ages out” it uses the oldest of the found set, so 24 day old listing is preferred to a 1 day old listing, if they are identical.