Modify structs – test with assert_eq! macro
This Rust code defines a simple struct called Coord and implements some methods for it. The Coord struct has two fields, x and y, representing coordinates in a two-dimensional space.
Create the struct
#![allow(unused)]
#[derive(Debug,PartialEq)]
struct Coord {
x: f32,
y: f32,
}Make an implementation
The Coord::new() function is a constructor method that creates a new Coord instance with initial values of x set to 12.2 and y set to 231.2. This method is called without any arguments and returns a new Coord object.
impl Coord {
fn new() -> Self {
Coord { x: 12.2, y: 231.2 }
}
// mut !
// returns nothing!
fn add(&mut self){
self.x += 3.9;
self.y +=21.1;
}
}The Coord::add(&mut self) method takes a mutable reference to a Coord object as its parameter. It modifies the x and y fields of the Coord object by adding 3.9 to x and 21.1 to y. This method is denoted as mutating the object with the &mut reference and doesn’t return anything.
Main
In the main function, a mutable variable c1 is declared and initialized with a new Coord object created using Coord::new(). Then, the add method is called on c1 to update its coordinates. Finally, the println! macro is used to print the updated c1 object.
fn main() {
let mut c1 = Coord::new();
// v name + add!
c1.add();
println!("{:?}",c1);
}In summary, this Rust code demonstrates the creation of a simple Coord struct, the implementation of a constructor method, and a mutating method, and how to use these methods in the main function to manipulate and display coordinates.
Test the function
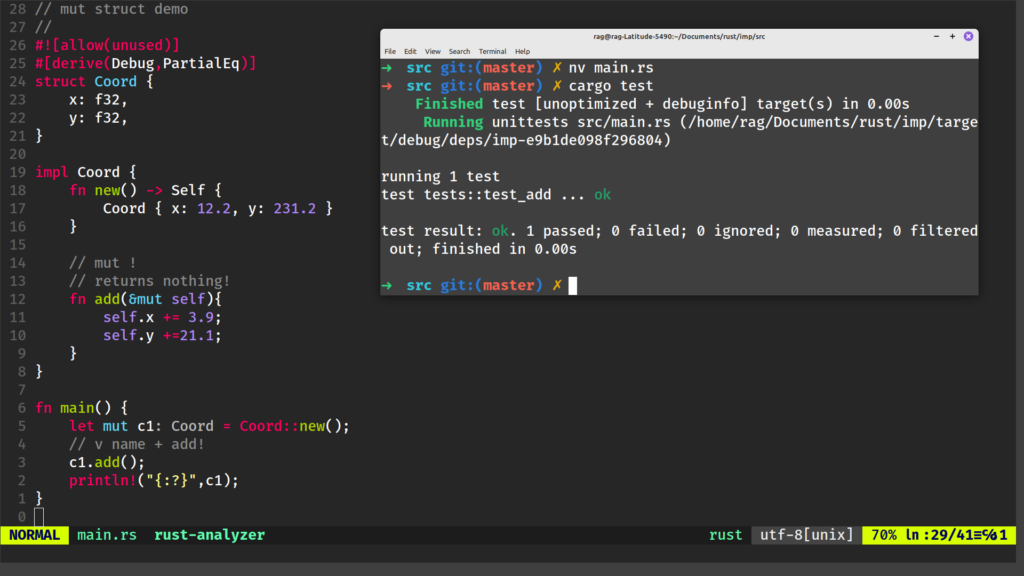
This code below defines a test module named tests, used for testing. It imports items from the parent module, likely containing the Coord struct. Inside, there’s a test function named test_add. It initializes a mutable Coord object, applies the add method, and checks if the resulting coordinates match { x: 16.1, y: 252.3 } using the assert_eq! macro. If the assertion fails, the test fails, indicating an issue with the add method or Coord implementation. This code ensures the correctness of the add method through automated testing when running Rust unit tests.
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use super::*;
#[test]
fn test_add(){
let mut c1 = Coord::new();
c1.add();
assert_eq!(c1, Coord { x: 16.1, y: 252.3 });
}
}Output